Glaucoma: Frequently Asked Questions
- What is glaucoma?
- What is the optic nerve?
- What is open-angle glaucoma?
- Does increased eye pressure
mean that I have glaucoma? - Will I develop glaucoma if
I have increased eye pressure? - Can I develop glaucoma without
an increase in my eye pressure? - Who is at risk for open-angle glaucoma?
- How can I prevent the disease from occurring?
- What are the symptoms of glaucoma?
- How is glaucoma detected?
- Can glaucoma be cured?
- Can glaucoma be treated?
- What can I do to protect my vision?
- What can I do if I already have
lost some vision from glaucoma? - What research is being done?
- What should I do for a family member or friend
who may be at risk of glaucoma? - Does Medicare cover the cost
of an annual comprehensive eye exam? - Where can I get more information?
Glaucoma is a group of diseases that can damage the eye's optic nerve and result in vision loss and blindness. The most common form of the disease is open-angle glaucoma. With early treatment, you can often protect your eyes against serious vision loss.
The optic nerve is a bundle of more than 1 million nerve fibers. It connects the retina to the brain.
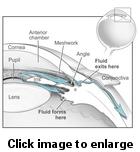
Open-angle glaucoma is the most common form of glaucoma. In the normal eye, the clear fluid leaves the anterior chamber at the open angle where the cornea and iris meet. When the fluid reaches the angle, it flows through a spongy meshwork, like a drain, and leaves the eye.
Does increased eye pressure mean that I have glaucoma?
Not necessarily. Increased eye pressure means you are at risk for glaucoma, but does not mean you have the disease. A person has glaucoma only if the optic nerve is damaged. If you have increased eye pressure but no damage to the optic nerve, you do not have glaucoma. However, you are at risk. Follow the advice of your eye care professional.
Will I develop glaucoma if I have increased eye pressure?
Not necessarily. Not every person with increased eye pressure will develop glaucoma. Some people can tolerate higher eye pressure better than others. Also, a certain level of eye pressure may be high for one person but normal for another.
Can I develop glaucoma without an increase in my eye pressure?
Yes. Glaucoma can develop without increased eye pressure. This form of glaucoma is called low-tension or normal-tension glaucoma. It is not as common as open-angle glaucoma.
Who is at risk for open-angle glaucoma?
Anyone can develop glaucoma. Some people are at higher risk than others. They include:
- African-Americans over age 40
- everyone over age 60, especially Mexican-Americans
- people with a family history of glaucoma.
- inflammation or uveitis in the eye, or a history of eye trauma
- people with diabetes, myopia (nearsightedness), or extensive steroid use
How can I prevent the disease from occurring?
At this time, we do not know how to prevent glaucoma. However, studies have shown that the early detection and treatment of glaucoma, before it causes major vision loss, is the best way to control the disease. So, if you fall into one of the high-risk groups for the disease, make sure to have your eyes examined through dilated pupils every two years by an eye care professional.
What are the symptoms of glaucoma?
At first, open-angle glaucoma has no symptoms. It causes no pain. Vision seems normal.
Glaucoma is detected through a comprehensive eye exam that includes a visual acuity test, visual field test, dilated eye exam, tonometry, and pachymetry.
No. There is no cure for glaucoma. Vision lost from the disease cannot be restored.
Yes. Immediate treatment for early stage, open-angle glaucoma can delay progression of the disease. That's why early diagnosis is very important. Glaucoma treatments include medicines, laser surgery, conventional surgery, or a combination of any of these. While these treatments may save remaining vision, they do not improve sight already lost from glaucoma.
What can I do to protect my vision?
If you are taking medicines for glaucoma, be sure to take them every day as directed by your eye care professional. People at risk for glaucoma should have a dilated eye exam at least every two years. If you have been diagnosed, you may need to see your eye care professional more often.
What can I do if I already have lost some vision from glaucoma?
If you have lost some sight from glaucoma, ask your eye care professional about low vision services and devices that may help you make the most of your remaining vision.
Through studies in the laboratory and with patients, the National Eye Institute is seeking better ways to detect, treat, and prevent vision loss in people with glaucoma. For example, researchers have discovered genes that could help explain how glaucoma damages the eye.
What should I do for a family member or friend who may be at risk of glaucoma?
Encourage them to have a comprehensive dilated eye exam at least once every two years. Remember -- lowering eye pressure in glaucoma's early stages slows progression of the disease and helps save vision.
Does Medicare cover the cost of an annual comprehensive eye exam?
Yes, in certain cases. Medicare covers an annual comprehensive dilated eye exam for some people at high risk for glaucoma. These people include those with diabetes, those with a family history of glaucoma, and African-Americans age 50 and older.
Where can I get more information?
National Eye Institute |
The Glaucoma Foundation |
Glaucoma Research Foundation |
*Information from National Institutes of Health